400-007 Exam Dumps - Cisco Certified Design Expert (CCDE v3.1)
Searching for workable clues to ace the Cisco 400-007 Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s 400-007 PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
Which optimal use of interface dampening on a fast convergence network design is true?
In a redundant hub-and-spoke design with inter-spoke links, load oscillation and routing instability occur due to overload conditions. Which two design changes improve resiliency? (Choose two)
A large enterprise is planning a new WAN connection to headquarters. The current dual-homed setup with static routing is not providing consistent resiliency. Users complain when one specific link fails, while failure of the other causes no issues. The organization wants to improve resiliency and ROI.
Which solution should be recommended?
What are two advantages of controller-based networks versus traditional networks? (Choose two.)
Company ABC wants to minimize the risk of users plugging unauthorized switches and hubs into the network. Which two features can be used on the LAN access ports to support this design requirement? (Choose two.)
A large enterprise cloud design team is evaluating cloud consumption models. What is an example of a typical PaaS limitation or concern?
Refer to the exhibit.
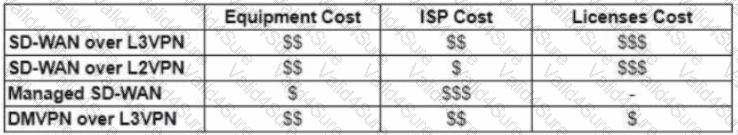
The WAN network of the General Bank of Greece has experienced several outages. It takes too long to activate a new branch site. The networking department of the bank plans to upgrade the legacy end-of-life WAN network with a new flexible, manageable, and scalable in-house solution. The number of branches will increase exponentially in the next fiscal year. The CTO states that the bank’s main goal is OPEX reduction. The network engineering team prepares a table to evaluate the available options. Which WAN technology can be used for the solution?