Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer Exam Dumps - Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Network Engineer
Searching for workable clues to ace the Google Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
You want to implement an IPSec tunnel between your on-premises network and a VPC via Cloud VPN. You need to restrict reachability over the tunnel to specific local subnets, and you do not have a device capable of speaking Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Which routing option should you choose?
In order to provide subnet level isolation, you want to force instance-A in one subnet to route through a security appliance, called instance-B, in another subnet.
What should you do?
You have just deployed your infrastructure on Google Cloud. You now need to configure the DNS to meet the following requirements:
Your on-premises resources should resolve your Google Cloud zones.
Your Google Cloud resources should resolve your on-premises zones.
You need the ability to resolve “. internal†zones provisioned by Google Cloud.
What should you do?
Question:
Your organization wants to deploy HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect to ensure encryption in transit over the Cloud Interconnect connections. You have created a Cloud Router and two encrypted VLAN attachments that have a 5 Gbps capacity and a BGP configuration. The BGP sessions are operational. You need to complete the deployment of the HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect. What should you do?
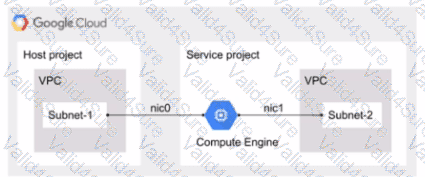
You have the following Shared VPC design VPC Flow Logs is configured for Subnet-1 In the host VPC. You also want to monitor flow logs for Subnet-2. What should you do?