EFM Exam Dumps - Certified - Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Searching for workable clues to ace the NCC EFM Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s EFM PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
Tachysystole can have a negative effect on fetal oxygenation during labor by
An internal electronic fetal monitor tracing continues to record artifact despite equipment troubleshooting and replacement of the spiral electrode. The next action is to:
A sentinel or reportable event as defined by the Joint Commission or other regulatory bodies/agencies is one that
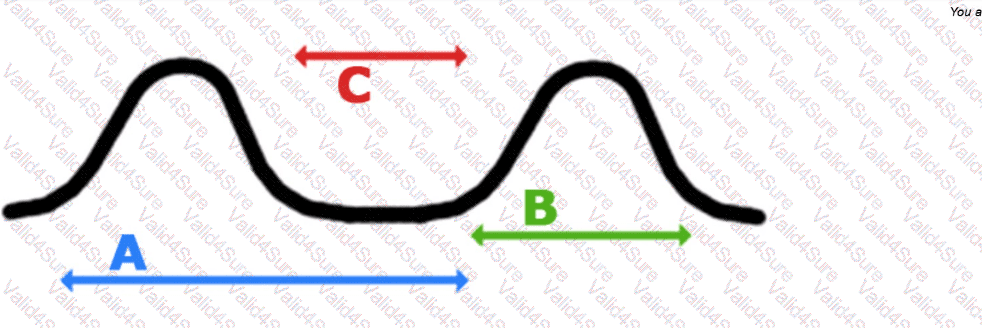
A fetus displays a baseline heart rate of 125 beats per minute with moderate variability. During a contraction, the baseline rate drops abruptly to 80 beats per minute with gradual return to baseline over 90 seconds. This is classified as: