EFM Exam Dumps - Certified - Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Searching for workable clues to ace the NCC EFM Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s EFM PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
This fetal heart rate tracing is from a woman in the second stage of labor. This tracing is best interpreted as:
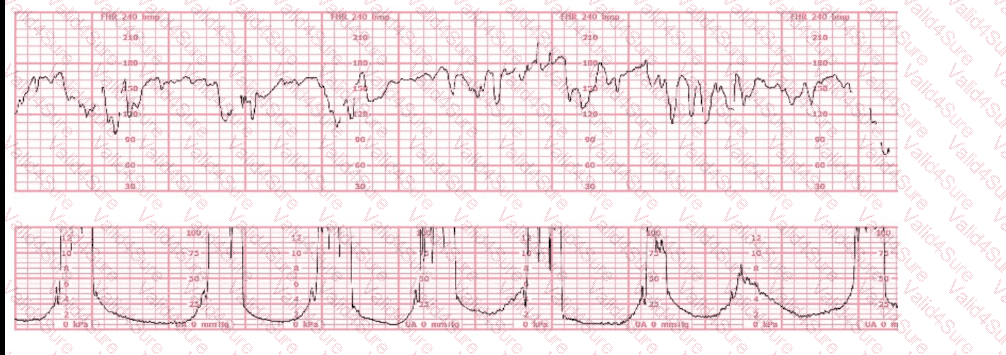
The most probable underlying fetal physiologic cause for this tracing would be:
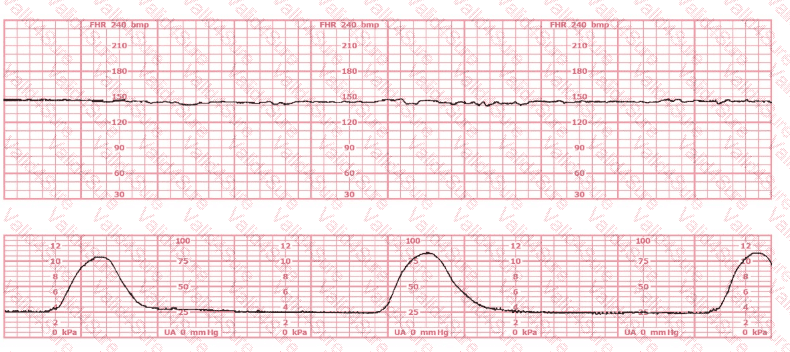
A fetal heart rate pattern characteristic of fetal neurological injury and impending intrapartum fetal demise is:
(Full question statement)
The fetal heart rate tracing shown is obtained upon the woman's admission to labor and delivery. This tracing is most consistent with what maternal condition?
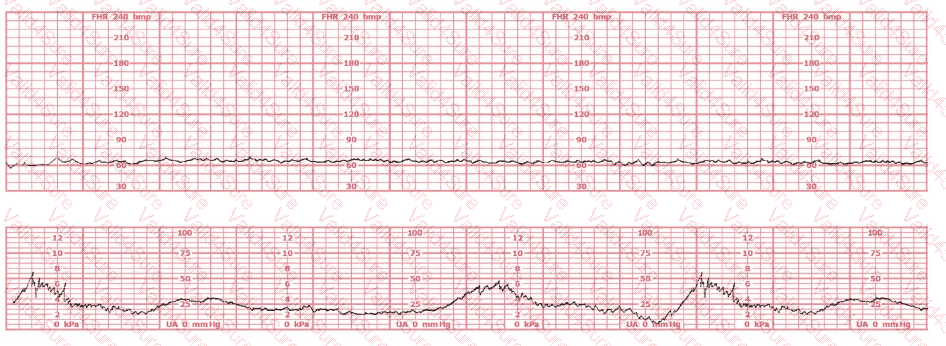
A patient presents at 38-weeks gestation with complaints of decreased fetal movement and ruptured membranes. The fetal heart rate is not able to be determined with an external ultrasound monitor. A spiral electrode is placed, and the tracing shows a rate of 90 bpm. What is the next most appropriate action?