P1 Exam Dumps - Management Accounting
Searching for workable clues to ace the CIMA P1 Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s P1 PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
A company is forecasting sales volume using time series analysis. The following equation has been derived from past data and is considered to be a reliable predictor of future sales volume:
y = 20,000+80x
Where y is the total sales units each quarter and x is the time period (the first quarter of year 1 is time period 1).
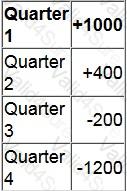
The following set of seasonal variations for each quarter has been calculated using the additive model.
What is the forecast sales units for the second quarter of year 3?
A museum charges a reduced entrance fee for students in full-time education. The budgeted cost per customer is the same regardless of the entrance fee paid.
4,000 customers were budgeted to visit the museum during period 6, with 25% of customers paying the reduced fee.
3,000 customers visited the museum during period 6 and 1,000 of these paid the reduced entrance fee. Costs were as budgeted but the actual full-priced entrance fee was $2 higher than budgeted.
Which of the following statements is true?
A company manufactures a range of products. It is deciding whether to make one of its products internally or to buy the product partially completed from an external source and complete the manufacture in-house. The table below gives details of the variable costs of the two alternatives. Fixed production costs will remain the same under both alternative.
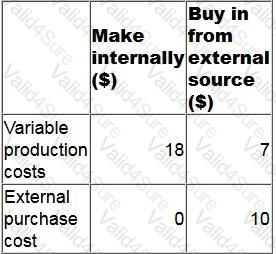
What is the sensitivity of the decision to a change in the external purchase price?
Give your answer as a whole percentage.
Product G has the following sales information:
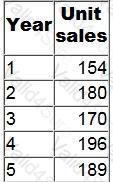
If moving averages of annual sales over 3-year periods are calculated, what is the moving average at Year 3?
TP makes wedding cakes that are sold to specialist retail outlets which decorate the cakes according to the customers’ specific requirements. The standard cost per unit of its most popular cake is as follows:
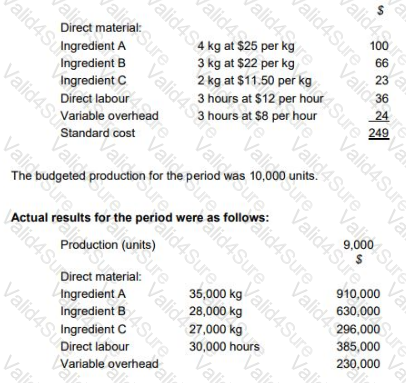
The general market prices at the time of purchase for Ingredient A and Ingredient B were $23 per kg and $20 per kg respectively. TP operates a JIT purchasing system for ingredients and a JIT production system; therefore, there was no inventory during the period.
Discuss the usefulness of the planning and operational variances calculated for TP’s management.
Select ALL the TRUE statements.