A00-240 Exam Dumps - SAS Statistical Business Analysis SAS9: Regression and Model
Searching for workable clues to ace the SAS Institute A00-240 Exam? You’re on the right place! ExamCert has realistic, trusted and authentic exam prep tools to help you achieve your desired credential. ExamCert’s A00-240 PDF Study Guide, Testing Engine and Exam Dumps follow a reliable exam preparation strategy, providing you the most relevant and updated study material that is crafted in an easy to learn format of questions and answers. ExamCert’s study tools aim at simplifying all complex and confusing concepts of the exam and introduce you to the real exam scenario and practice it with the help of its testing engine and real exam dumps
This question will ask you to provide a segment of missing code.
The following code is used to create missing value indicator variables for input variables, fred1 to fred7.

Which segment of code would complete the task?

The following LOGISTIC procedure output analyzes the relationship between a binary response and an ordinal predictor variable, wrist_size Using reference cell coding, the analyst selects Large (L) as the reference level.
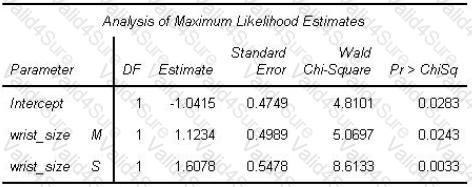
What is the estimated logit for a person with large wrist size?
Click the calculator button to display a calculator if needed.
Which of the following describes a concordant pair of observations in the LOGISTIC procedure?
What is the default method in the LOGISTIC procedure to handle observations with missing data?